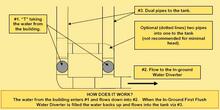
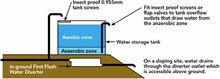
Buried and out of sight, In-Ground Water Diverters are perfect for sloping allotments. On a site that provides the opportunity for the end cap of the diverter to be positioned above ground (to drain out and be accessible for maintenance), an In-Ground Diverter allows a ‘wet’ system to be converted into a ‘dry’ system.
Most systems are ‘wet’ due to the size of buildings, and the placement of tanks away from the buildings means that there are long runs of pipes underground leading to a riser at the tank. On a sloping site, this diverter ensures the diverted water and the water that would normally remain in the pipes empties out. The result – is a ‘dry’ system that improves water quality.
Features and Benefits
- Prevents sediment, bird droppings, spiders, insects, mosquito eggs and debris from entering the rainwater tank.
- Improves water quality, and protects pumps and internal appliances.
- Ideal to use in conjunction with a rain head.
- Perfect for sloping allotments.
- No mechanical parts.
- Inlet fits 90mm pipe or 100mm female fitting.
- Simple to install – just add 300mm diameter pipe and glue. (300mm pipe can also be purchased from Bluewater Tanks)
- Low maintenance.
- Converts a ‘wet’ system into a ‘dry’ system.

How much water to divert
It is important to prevent heavy sediments and other roof pollutants from entering the rainwater tank. It is recommended that the amount of water diverted should be a minimum of 20 litres per 100 square metres of roof area (or 0.2L per m2). In calculating the amount of water to divert, consideration can be given to (1) the surface area of the roof, and (2) the number of pollutants on the roof and gutters.
The following factors can be used as a guide in determining the volume of water to be diverted.
- Pollution Factor For The Roof
- Minimal pollution – Divert 0.5 litres per square metre (open fields, no trees, no bird droppings, clean environment)
- Substantial pollution – Divert 2 litres per square metre (leaves and debris, bird droppings, various animal matter)
- Diversion Factor for a first flush water diverter – m2 Roof Area x Pollution Factor = Litres to be diverted
- Example for a minimal polluted roof of 100m2 – 100 x 0.5 = 50 litres to be diverted
- Example for a heavily polluted roof of 100m2 – 100 x 2 = 200 litres to be diverted
As a rule of thumb, the more water that is diverted the better the quality of water in the tank.
Multi pipe feed systems
These water diverters can handle more than one pipe
Single or multiple pipes carrying water from the roof can be directed into an In-Ground Water Diverter.

Installation Instructions
Determine the length of the 300mm pipe required using the table below.
Inlet End: The ball seat #6 is inserted into the top of the end cap as shown.
- For 90mm infeed – insert the ball seat #6 and attach the infeed pipe hard down on top of ball seat #6.
- For 100mm infeed – insert the ball seat #6 and glue the 90mm keeper ring (28mm long) hard down on top of the ball seat #6 to keep it firmly in place.
Outlet End: The outlet requires only a 90mm pipe. Assemble as shown in the attached drawing making sure to insert ball #7 before attaching cap #11. Select one of the four control valves #12 and fit it into hose connector #13. Save the remaining valves for possible later use.